Used to determine the presence of a sacroiliac and/or iliosacral dysfunction With the patient seated laying supine, physician will find the anterior superior iliac spines (ASIS), and physician will place their palm on top of the ASIS on both sides. The physician will then exert a posterior compressive force on each of […]
Category: Diagnostic Tools
Used to assess for leg length discrepancy With the patient supine, the patient brings the knees so that they are equally flexed to 90 degrees with the hips at roughly 45 degrees of flexion If the heights vary, there may be a leg length discrepancy One leg more anterior on lateral view, […]
Used to determine is the state of the subclavian artery Steps: Patient is standing or seated Patient is instructed to abduct the shoulders to 90 degrees, externally rotate, and flex the elbows Instruct the patient to flex and extend their fingers for up to 3 minutes Physician watch for discoloration […]
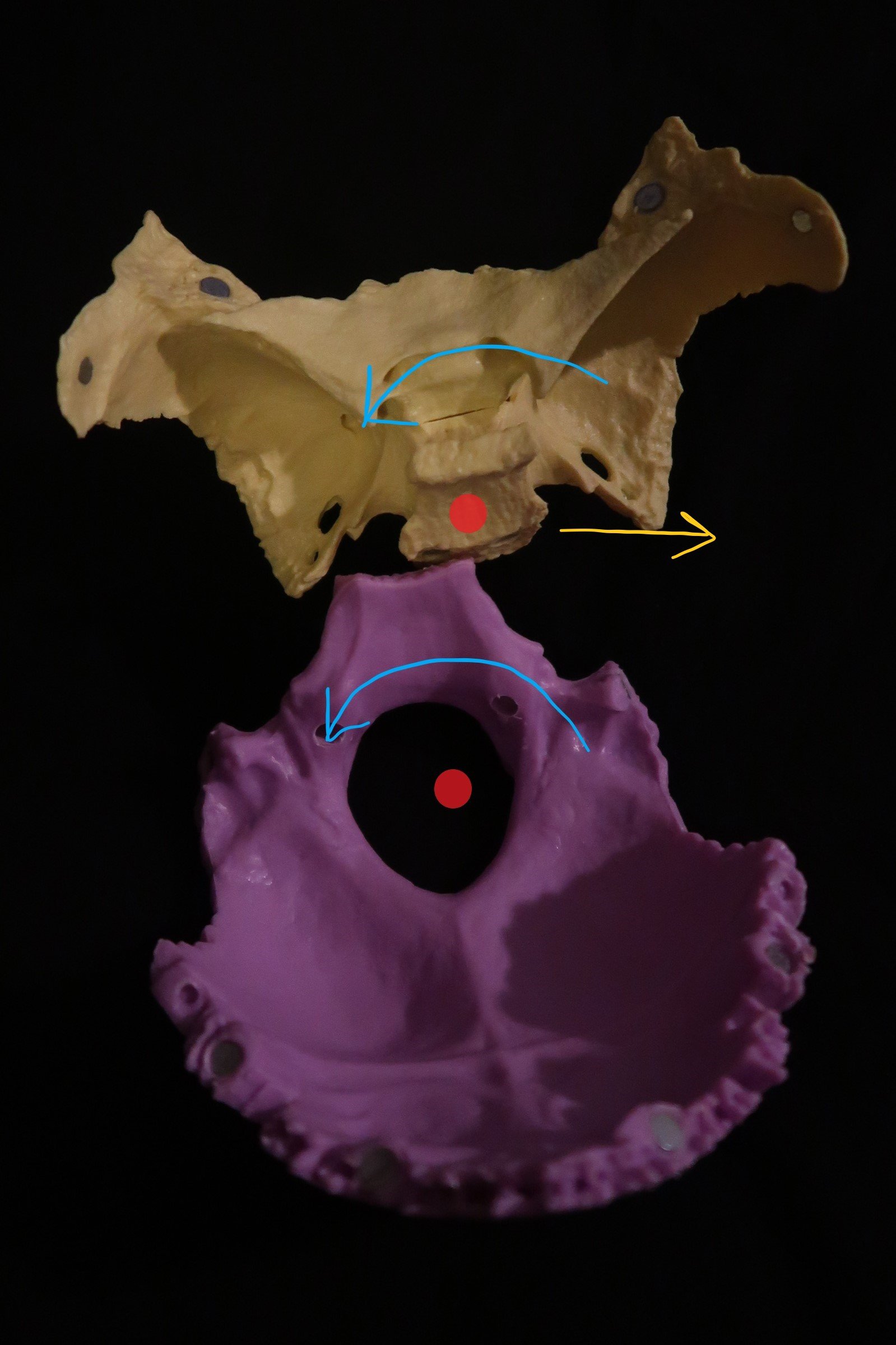
Overview 2 parallel vertical axises (red circles/lines in images below) 1 through the foramen magnum (occipital bone, purple bone below) 1 through the body of the sphenoid (white bone below) Sphenoid and occiput rotate in the same direction about their vertical axises (clockwise, counterclockwise) Naming The naming of a vertical strain […]
Overview 2 parallel transverse axes (red lines in images below) 1 axes through the sphenoid bone (purple bone below) 1 axes through the occipital bone (white bone below) Naming The naming of a vertical strain is based on the position of sphenoid base in relation to occiput (superior or inferior). […]
Overview Results from compression of the sphenoid and occiput at the SBS junction Etiologies Trauma (back/front of head) Circumferential compression (childbirth) SBS Compression Hand Motion Skull Motion
Who came up with Osteopathy in the Cranial Field? William Garner Sutherland What are the five body components of PRM (primary respiratory mechanism)? The inherent motility of the brain and spinal cord (CNS) Fluctuation of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Mobility of the intracranial and intraspinal membranes (RTM) Articular mobility of […]
Overview All cranial movements are named for the movement of the sphenobasilar synchondrosis (SBS), the articulation of the sphenoid bone and occiput This movement is the palpable Cranial Rhythmic Impulse This is the basis of the physiologic strain patterns and pathologic strain patterns Skull White Bone = Sphenoid Purple Bone […]
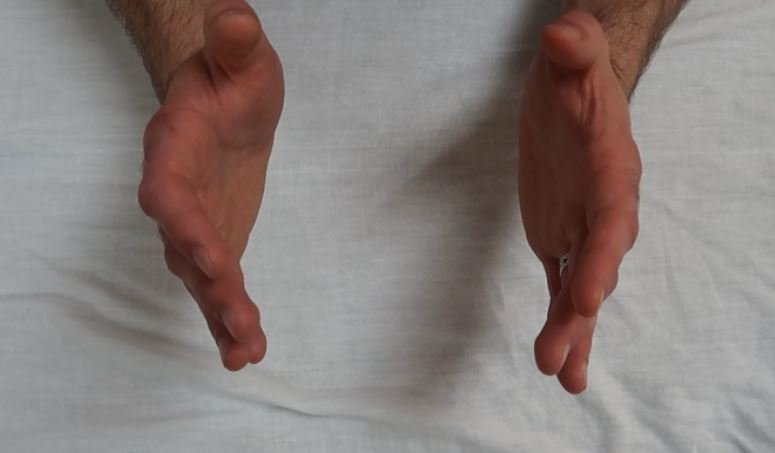
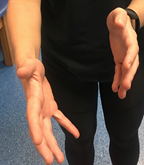
Overview Pathologic strain patterns are abnormal strain patterns and require treatment The 3 types of pathologic strain patterns are: Vertical Strains Lateral Strains Sphenobasilar Compression In a lab setting, you will be asked to demonstrate these motions using your hands On a written or oral exam, you may be asked […]
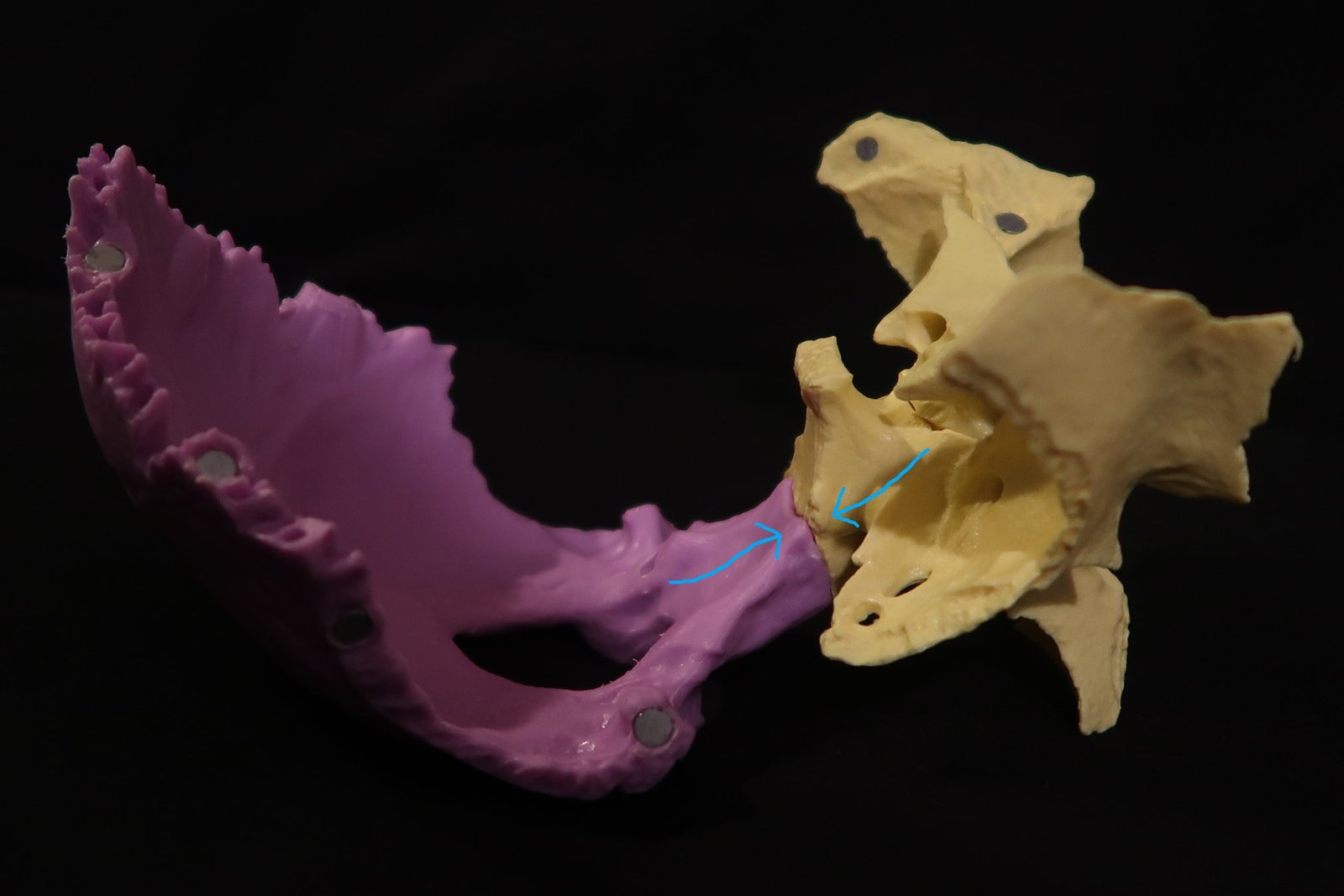
Overview Number of Axises = 3 Type of Axis Sidebending – 2 parallel vertical axises 1 through foramen magnum (occipital bone) 1 through body of sphenoid Sphenoid and occiput rotate in opposite directions about vertical axes (clockwise, counterclockwise) Rotation – 1 Anteroposterior (AP) axis AP axis through the sphenoid and […]
Overview Number of Axes = 1 Type of Axes = 1 Anteroposterior (AP) axis through the sphenoid and occiput The sphenoid and occiput rotate in opposite direction about this single AP axis Naming The naming of cranial torsions is based on the side with the higher wing of the sphenoid […]
Overview 2 parallel transverse axes (red lines in images below) 1 axes through the sphenoid bone (purple bone below) 1 axes through the occipital bone (white bone below) Naming The naming of cranial flexion/extension motion is based on flexion or extension of the midline bones of the skull (sphenoid, occipital, […]
Overview Physiological strain patterns are “normal” types of cranial motion The 3 types of physiologic motions are: Flexion/Extension Torsions Sidebending/Rotation In a lab setting, you will be asked to demonstrate these motions using your hands On a written or oral exam, you may be asked to indicate the number of […]
The Position The student doctor is seated at the side of the head of the table with the patient placed in a supine position. With his/her forearm resting on the table, the student doctor advances his/her caudad hand under the patient’s occiput. This establishes a fulcrum. With his/her elbow resting […]
Flexion / External Rotation Coronal Diameter – increases (widens) Anteroposterior Diameter – decreases Height – decreases Extension / Internal Rotation Coronal Diameter – decreases Anteroposterior Diameter – increases (widens) Height – increases Normal CRI CRI = Cranial Rhythmic Impulse Normal Amplitude of CRI is 8-14 cycles per minute For a […]
The Position The student doctor is seated at the head of the table with the patient placed in a supine position. Position the patient far enough down on the table so the student doctor can rest his/her forearms on the table. The student doctors places their hands on the patient’s […]
Anatomy Function Quadricep muscles are hip flexors and knee extensors. Innervation The quadricep muscles are innervated by the femoral nerve (L2-L4). Prone Muscle Test Patient in prone with physician at side of table Monitor the pelvis at the PSIS so it does not rise Bring ankles toward the patient’s buttock, […]
Anatomy Function Hamstring muscles are hip extensors. Innervation The hamstring muscles are innervated by sciatic nerve (L5, S1-S2). Method One Patient supine with their hip flexed at a 90 degree angle and knee bent Attempt to straighten the knee out vertically with the hip still flexed at a 90 degrees […]
Overview Function Piriformis is a lateral/external rotator of the hip joint. Innervation Levels: L5, S1-S2 Sciatic nerve often runs through or behind the piriformis muscle Supine Muscle Testing Patient lies supine Grasp above the ankles bilaterally (important to grab above the ankle joint) Using the lower extremity, internally rotate each […]
Steps in Evaluating Scoliosis: Patient is standing with a chair or stool placed in front of them Physician is behind the patient Ask the patient to bend forward Observe for a posterior rib angle AT EYE LEVEL – Physician may need to be seated or kneel to ensure being at eye […]
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is the #1 Most common Entrapment Neuropathy Common Patient Presentation Repetitive overuse of wrist (seamstress, secretary, etc.) Pregnant patient with edema Diabetic Patients Pain of carpal tunnel syndrome is usually worse at night Results in paresthesias of lateral 3 and 1/2 fingers and distal portion of palm with […]
Fibular Head Dysfunctions Fibular Head Somatic Dysfunction is commonly seen after a medial ankle sprain, forced dorsiflexion, and/or in genu recurvatum A few good mnemonics for understanding the fibular head dysfunctions are AEED and PIIP AEED: Anterior fibular head is externally rotated, everted, and dorsiflexed PIIP: Posterior fibular head is internally […]
Radial Head Dysfunctions A good mnemonic for understanding the radial head dysfunctions is SAPP SAPP refers to the freedom of motion (remember all somatic dysfunctions are named in the freedom of motion) not the position necessary for treatment Radial head “wants” to be in Supination→ Anterior radial head Radial head […]
Fryette’s Principles Both the thoracic and lumbar spine follow Fryette’s Principles Thoracic and lumbar spine diagnoses are a tri-planar and include: Rotation, Sidebending, and Flexion/Extension Flexion and Extension will only apply to a Type II “Non-Neutral” Dysfunction However, in order to differentiate between Type I and Type II dysfunctions, it is important to […]
A good mnemonic to remember: “Eating Fried Chicken makes ABs ADd Inches Definitely” Steps: Know the exact order! Shoulder extension with elbow flexed Doctors cephalad hand stabilizes the acromioclaviular + scapulothoracic joints to prevent their motion = isolates the glenohumeral joint Shoulder flexion with elbow extended Doctor continues to stabilize […]
“Costovertebral angle tenderness“ Used to assess for a pyelonephritis, kidney stone, or other kidney pathology With the patient seated and slightly flexed, a percussive force is applied to the back between T9-12 Positive with pain
Tests for gallbladder pathology Patient supine, examiner placed a hand beneath the right costal margin anterior at the midclavicular line and applies a force superiorly beneath the rib cage and into the gallblader. Patient is instructed to take a deep breath in, Positive sign is when the patient pauses during inspiration […]
Kernig’s Test With the patient supine, passively raise the leg with the knee extended Positive if patient is forced to flex head with leg raise Video Tutorial for Kernig’s Test: Brudzinski Test Patient supine, head is passively flexed Positive if patient flexes hips and knees with head flexion Video Tutorial […]
Clinical manifestation of hypocalcemia which creates a state of hyper-excitability (tetany) of the facial nerve With the patient seated, the examiner taps on the side of the face over the cheek Positive for involuntary wincing of the face with gentle tapping
•Use a firm object – scrape from calcaneal distal on the lateral side•Cross over at the ball of the foot Tests for Upper Motor Neuron Injury A positive test is when the toes flair cephalad and spread out. A negative test is when the toes curl towards plantar surface of the foot […]
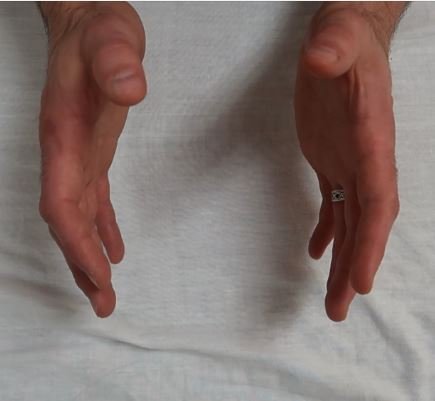
•Tests for Upper Motor Neuron Patient’s hand is supported and relaxed with the wrist extended and the middle finger slightly flexed The middle finger is flicked from dorsal to volar Positive test = the thumb and index finger approximation as if the finger pads are going to touch
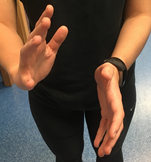
Test for adequate circulation of the arteries of the hand First the radial and ulnar arteries need to be palpated. Then, both arteries are blocked by the examiner applying sufficient pressure while the patient makes a fist. This forces all of the blood out of the hand. Next, the patient relaxes their […]
Tests for DeQuarvain Tenosynovitis Steps: Have the patient close their fingers around their thumb Doctors holds on patients hand to ulnar deviate the wrist to put a pull on the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus Test is considered to be positive if pain is reproduced indicating tenosynovitis
Used to test for impingement of the median nervein the carpal tunnel Phalen Test: Patient is instructed to place the dorsal surfaces of the hands together and fully flex the wrists. This position is to be held for 60 seconds or until numbness/tingling of the hand(s) is felt, whichever is shorter Reverse […]
Used to assess for neuropathy or median nerve compression In the hand, the wrist is passively extended, and a tapping force is applied directly over the flexor retinaculum Test is considered to be positive if pain or paresthesias are reproduced within the median nerve distribution May be used in other areas of […]
Used to assess for neuropathy or nerve compression Test is performed by forcefully tapping at the cubital tunnel between the medial epicondyle of the humerus and the olecranon. Positive if symptoms of pain or paresthesias are reproduced in the ulnar nerve distribution.
Used to determine is the state of the subclavian artery Steps: The test is considered to be positive if the radial pulse weakens or fades completely. Positive test indicates there is compression of subclavian artery (Arterial component of Thoracic Outlet Syndrome) Video Tutorial:
Used to assess for acromioclavicular joint pathology Steps Physician passively places the arm into 90 degrees of forward flexion and adducts the arm until fully adducted across the chest with monitoring the AC joint with the other hand. The examiner may then gently add additional medially direcected force to further stress the […]
Used to determine labral, acromioclavicular (AC), or other anterior shoulder pathology Steps: Part one: Patient forward flexes the arm with the elbow extended. The patient then internally rotates the arm so THE THUMB IS POINTING DOWN. The patient then adducts the arm 5-10 degrees and resists the downward force applied by the […]
Used to determine active range of motion of the shoulder Steps: Patient may be seated or standing Ask the patient to first reach behind their back to try and reach the opposite shoulder 2. Next, have the patient reach across their chest to grab the other shoulder from the front. 3. […]
Used to detect tears in the rotator cuff muscles, particularly the supraspinatus Steps: Option 1 Patient fully abducts the arm, then is instructed to slowly lower the arm Test is considered to be positive if: patient’s arm with drop suddenly during the lowering of the arm (adduction back to the midline). Option […]
Used to assess whether or not the biceps tendon is stable within the groove, as well as for the presence of biceps tendinopathies Steps: Patient flexes the elbow to 90 degrees Examiner holds the elbow of the arm being tested in one hand, and with the other the physician externally rotates the arm and […]
Used to test for biceps tendinopathy Steps: Test is considered to be positive with pain at the shoulder/biceps tendon Video Tutorial:
Used to determine the integrity of the supraspinatus tendon Steps: Patient seated, physician standing Physician flexes patient’s shoulder and elbow 90° Physician internally rotates shoulder making sure it remains straight Test is considered to be positive if: pain upon internal rotation – indicates shoulder impingement
Used to test for supraspinatus or biceps brachii impingement Steps: With the patient’s arm forward flexed to 90 degrees and internally rotated so that the thumb is pointing downward, the examiner instructs the patient to continue flexion up toward the ceiling against physician resistance. Test is considered to be positive if: […]
A good mnemonic to remember: Feeling Extra Cold Today In Erie, Better ADd layers!” (note: Better is to remind you to ABduct before you ADduct!) Steps: Done in the specific order. Flexion (120°) Extension (30°) + support hip on other side Circumduction with compression: small circles → big circles (Counter-clockwise […]
Used to test the sciatic nerve for inflammation vs radicular pain or hamstring hypertonicity Begin with the patient supine, the leg is passively raised with the knee in full extension until the pain is reproduced. Pain in lower back indicates lumbar radiculopathy Continue by lowering the leg by approx 10 degrees, and […]
Used to determine if a sacral diagnosis is flexed or extended With the patient prone, the examiner monitors the sacral sulci while instructing the patient to extend by “getting up on your elbows like you’re going to watch tv.” Test is considered to be positive if the sulci do not even out, or if […]
Used to evaluate hypertonicity of the iliopsoas Begin with the patient supine, the patient takes both legs and passively flexes the knees and hip to flatten the lumbar lordosis. Remember to watch for increased lumbar lordosis (should not have this because it’s compensatory) – monitor this with placing your hand below […]
Used to test for hypertonicity of the quadriceps muscle, specifically the rectus femoris Similar to the Thomas Test, however this test is performed at the edge of the table Patient supine with gluteal crease near the edge of the table Have patient bring both knees to chest then let one leg […]